Embark on an enlightening journey with answers to everfi module 5, where financial literacy unfolds in a captivating narrative. This comprehensive guide unravels the intricacies of personal finance, empowering you to make informed decisions that shape your financial well-being.
Delving into the realm of financial literacy, we explore its significance in everyday life, unravel the complexities of financial accounts, and delve into the art of budgeting and saving.
Module Overview
Everfi Module 5 focuses on developing financial literacy skills. It introduces core concepts of personal finance, including budgeting, saving, investing, and managing debt. The module aims to equip individuals with the knowledge and tools to make informed financial decisions and achieve their financial goals.
Key objectives of the module include:
- Understanding the fundamentals of budgeting and cash flow management.
- Learning about different types of savings accounts and investment options.
- Recognizing the importance of managing debt responsibly.
- Developing strategies for financial planning and goal setting.
Section 1: Understanding Financial Literacy: Answers To Everfi Module 5
Financial literacy is a fundamental life skill that empowers you to make informed financial decisions and manage your money effectively. It’s not just about saving and investing; it’s about understanding how money works and how to use it wisely.
If you’re looking to ace EverFi Module 5, you might find the Edmark Level 1 Word List helpful. It provides a comprehensive vocabulary that can enhance your understanding of the module’s concepts. Once you’ve brushed up on these words, you’ll be well-equipped to tackle the EverFi Module 5 questions with confidence.
There are different types of financial accounts, each serving a specific purpose. Checking accounts allow you to access your funds quickly and easily for everyday expenses. Savings accounts help you build an emergency fund or save for future goals. Investment accounts, such as stocks and bonds, can help you grow your wealth over time.
Budgeting and Saving
Budgeting is the process of creating a plan for how you will spend your money each month. It involves tracking your income and expenses to ensure you’re living within your means and saving for the future. Saving is the act of setting aside a portion of your income for future use.
Whether it’s for an emergency fund, a down payment on a house, or retirement, saving is crucial for financial security.
Section 2: Managing Credit and Debt

In this section, we’ll delve into the world of credit and debt, exploring their impact on our financial health. We’ll uncover the various types of credit available, their advantages and disadvantages, and equip you with strategies for managing debt effectively.
Concept of Credit and Its Impact, Answers to everfi module 5
Credit refers to the ability to borrow money or access goods and services with the promise of paying later. It plays a crucial role in our financial lives, allowing us to make purchases we may not be able to afford upfront.
However, it’s essential to understand the potential impact of credit on our financial well-being.
Using credit responsibly can help us build a positive credit history, making it easier to secure loans and favorable interest rates in the future. However, excessive or poorly managed credit can lead to debt, high interest payments, and damage to our credit score.
Types of Credit
There are various types of credit available, each with its unique features and terms:
- Credit Cards:Convenient and widely accepted, credit cards allow us to make purchases and pay later, typically with a monthly payment due date.
- Personal Loans:Unsecured loans that provide a lump sum of money, to be repaid over a fixed period with regular installments.
- Mortgages:Long-term loans used to purchase real estate, secured by the property itself.
- Auto Loans:Loans specifically designed to finance the purchase of a vehicle, secured by the vehicle itself.
Each type of credit has its pros and cons, so it’s important to carefully consider our needs and financial situation before choosing the right option.
Section 3: Investing for the Future
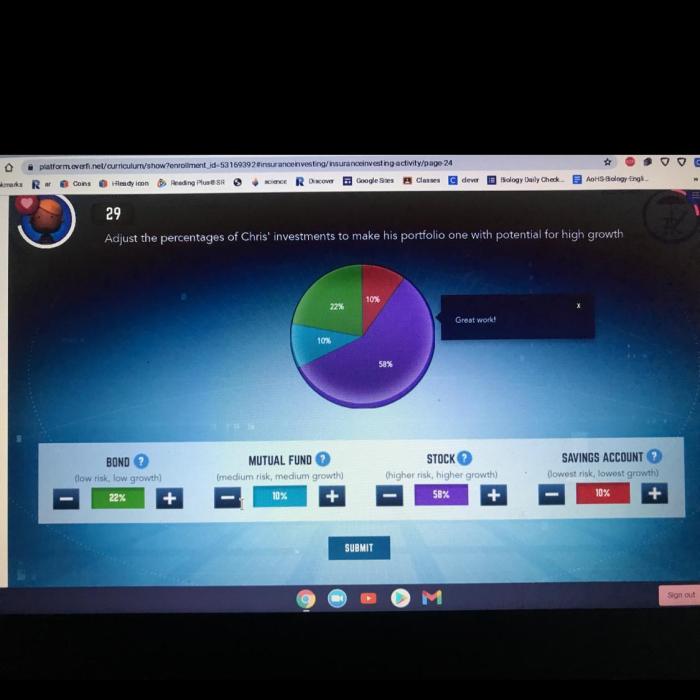
Investing is the act of allocating money with the expectation of generating profit or income. It’s a crucial aspect of financial planning, enabling individuals to grow their wealth and secure their financial future.
Basics of Investing
Investing involves two fundamental concepts: risk and return. Risk refers to the possibility of losing some or all of your invested capital, while return represents the potential profit or income you can earn. The higher the risk, the higher the potential return, and vice versa.
Types of Investments
There are numerous types of investments available, each with varying risk and return profiles. Common investment options include:
- Stocks:Represent ownership in a company and offer the potential for high returns but also carry higher risk.
- Bonds:Loans made to companies or governments, typically providing lower returns but with lower risk compared to stocks.
- Mutual Funds:Diversified portfolios of stocks, bonds, or other investments that offer a mix of risk and return.
- Real Estate:Land or property purchased for investment purposes, offering potential for appreciation and rental income.
Developing an Investment Strategy
Creating an investment strategy is crucial for maximizing your investment potential. Consider the following factors:
- Investment Goals:Define your financial objectives, such as retirement planning, education funding, or emergency savings.
- Risk Tolerance:Determine how much risk you’re willing to take based on your age, financial situation, and investment horizon.
- Time Horizon:Consider the length of time you plan to invest before needing the funds.
- Asset Allocation:Diversify your investments across different asset classes (e.g., stocks, bonds, real estate) to manage risk and enhance returns.
Section 4: Protecting Your Finances

In this digital age, protecting your financial assets from fraud and identity theft is crucial. Scammers are constantly devising new ways to steal your money and personal information. This section will provide you with essential knowledge to safeguard your finances and avoid becoming a victim of these malicious schemes.
Financial scams come in various forms, each designed to trick you into revealing sensitive information or parting with your hard-earned money. Understanding these scams and their tactics is the first step towards protecting yourself.
Types of Financial Scams
- Phishing Scams:These scams involve sending fraudulent emails or text messages that appear to come from legitimate sources like banks or government agencies. They often contain links that lead to fake websites designed to steal your login credentials or personal information.
- Identity Theft:This crime involves stealing someone’s personal information, such as their name, Social Security number, or credit card numbers, to commit fraud or other illegal activities.
- Investment Scams:Fraudulent schemes that promise high returns on investments with little to no risk. These scams often target vulnerable individuals who are looking for quick ways to make money.
- Credit Card Fraud:Unauthorized use of someone’s credit card to make purchases or withdrawals without their consent.
To protect yourself from these scams, it’s essential to be vigilant and take proactive measures to safeguard your personal and financial information.
Tips for Keeping Personal and Financial Information Secure
- Use Strong Passwords:Create complex passwords that are difficult to guess, using a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication:When available, use two-factor authentication to add an extra layer of security to your accounts. This requires you to provide a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your phone, when logging in.
- Be Cautious of Suspicious Emails and Text Messages:Never click on links or open attachments in emails or text messages from unknown senders. If you’re unsure about the legitimacy of a message, contact the sender directly through a trusted channel.
- Protect Your Social Security Number:Only share your Social Security number when absolutely necessary, and be mindful of who you provide it to.
- Monitor Your Credit Reports:Regularly check your credit reports from all three major credit bureaus to identify any suspicious activity or unauthorized inquiries.
- Shred Sensitive Documents:Before discarding any documents containing personal or financial information, shred them to prevent them from falling into the wrong hands.
- Use Secure Websites:When entering sensitive information online, make sure the website’s URL begins with “https” and has a padlock icon in the address bar, indicating a secure connection.
- Be Aware of Public Wi-Fi Networks:Avoid accessing sensitive financial information on public Wi-Fi networks, as they can be less secure than private networks.
By following these tips and staying informed about the latest financial scams, you can significantly reduce your risk of becoming a victim of fraud or identity theft. Protecting your finances is an ongoing process that requires vigilance and proactive measures.
Section 5: Real-World Application
Financial literacy skills are essential for navigating the complexities of modern life. They empower individuals to make informed financial decisions that can positively impact their well-being and financial stability.
Understanding financial concepts and principles enables individuals to manage their finances effectively, plan for the future, and protect themselves from financial risks. In this section, we will explore how financial literacy skills can be applied in real-world situations and the impact of financial decisions on individuals and families.
Case Studies and Examples
Consider the following case studies that illustrate the importance of financial literacy:
- Sarah’s Credit Card Debt:Sarah, a recent college graduate, accumulated significant credit card debt due to poor financial management. She struggled to make minimum payments and faced high interest rates, which further compounded her debt. With the help of a financial advisor, she created a budget, negotiated lower interest rates, and developed a plan to pay off her debt.
- John’s Retirement Planning:John, a 55-year-old engineer, realized he had not saved enough for retirement. By educating himself about retirement planning and investment options, he adjusted his budget, increased his contributions to his retirement account, and explored additional income streams to supplement his savings.
- Maria’s Insurance Coverage:Maria, a single mother, faced financial hardship after her car was totaled in an accident. Fortunately, she had adequate insurance coverage, which covered the repair costs and provided her with a rental car. This financial literacy enabled her to protect herself from a significant financial burden.
Impact of Financial Decisions
Financial decisions can have a profound impact on individuals and families:
- Positive Impact:Informed financial decisions can lead to financial stability, increased savings, reduced debt, and improved credit scores. These positive outcomes contribute to a higher quality of life and financial well-being.
- Negative Impact:Poor financial decisions, such as excessive debt, lack of savings, and inadequate insurance coverage, can result in financial stress, bankruptcy, and difficulty meeting financial obligations. These negative consequences can have long-lasting effects on individuals and families.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of financial literacy?
Financial literacy empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their finances, enabling them to manage their money effectively, plan for the future, and achieve their financial goals.
How can I improve my credit score?
To improve your credit score, make timely payments on all your debts, keep your credit utilization low, and avoid opening too many new credit accounts in a short period.
What is the best way to start investing?
To start investing, consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. Research different investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, and diversify your portfolio to mitigate risk.