How does switch spoofing work – Switch spoofing, a nefarious technique in the cyber realm, allows attackers to impersonate network devices by manipulating MAC addresses. Delve into the depths of this deceptive practice, unraveling its methods, consequences, and the crucial measures to combat it.
This comprehensive guide unveils the intricacies of switch spoofing, empowering you with the knowledge to safeguard your networks from this insidious threat.
Overview of Switch Spoofing
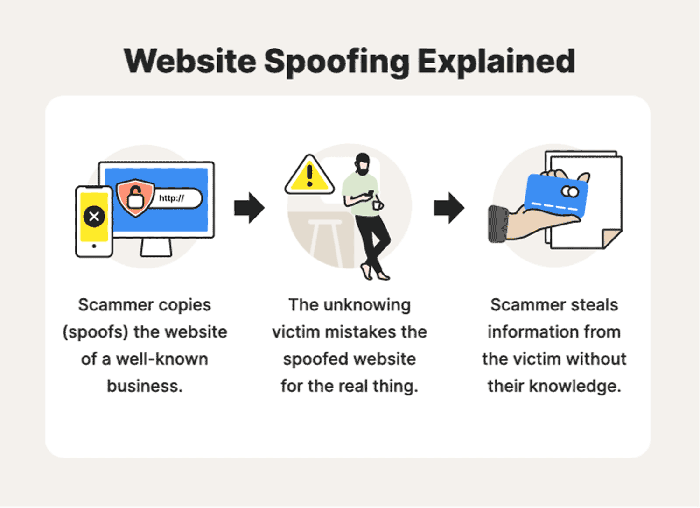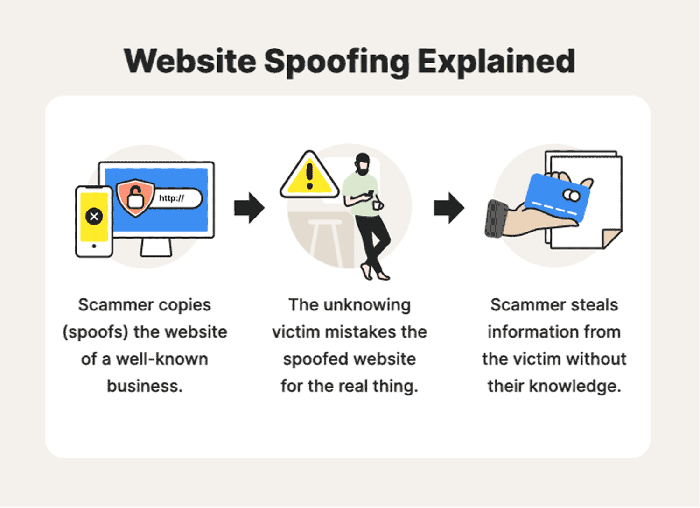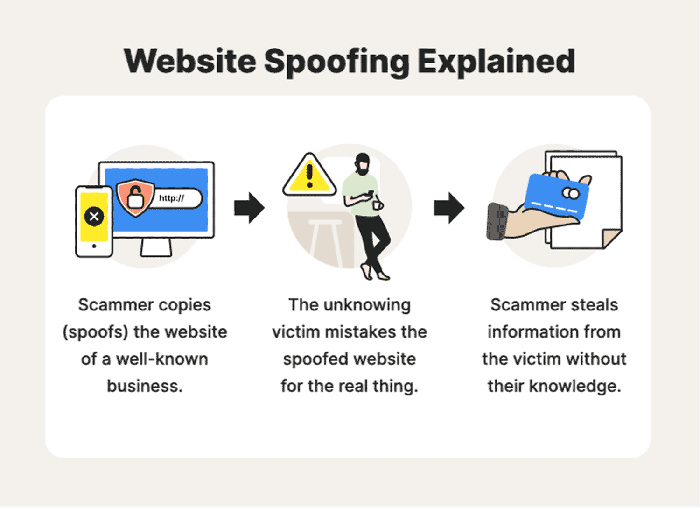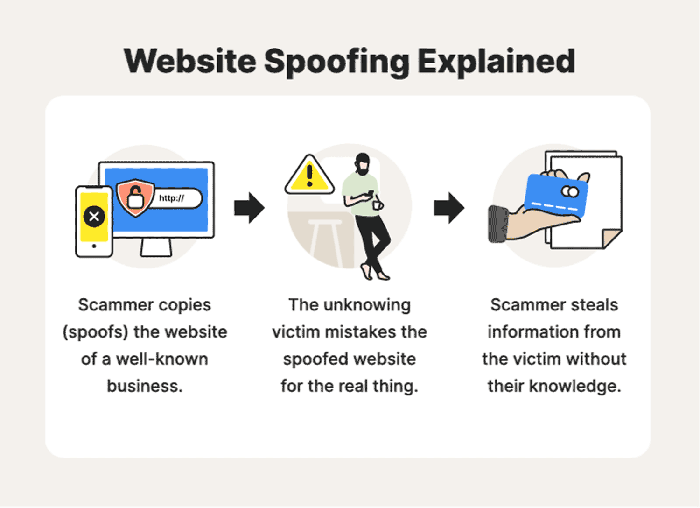
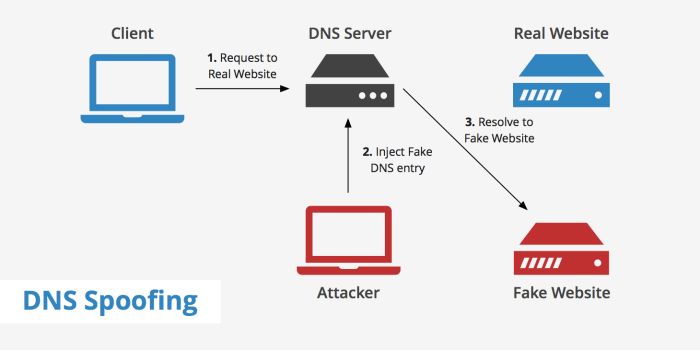
Switch spoofing is a malicious technique that allows an attacker to impersonate a network switch and manipulate network traffic. By doing so, the attacker can intercept, redirect, or modify data packets, leading to a range of security breaches.
Types of Switch Spoofing Attacks
There are several types of switch spoofing attacks, including:
- MAC Spoofing:The attacker spoofs the MAC address of a legitimate switch to gain unauthorized access to the network.
- IP Spoofing:The attacker spoofs the IP address of a switch to redirect traffic or bypass security measures.
- ARP Spoofing:The attacker spoofs the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) to map IP addresses to MAC addresses, allowing them to intercept or redirect traffic.
Real-World Applications of Switch Spoofing
Switch spoofing can be used in various real-world attacks, such as:
- Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks:The attacker intercepts traffic between two devices and impersonates one of them to steal sensitive information.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks:The attacker floods the network with spoofed traffic to overwhelm switches and disrupt network connectivity.
- Malware Distribution:The attacker spoofs the switch to redirect traffic to malicious websites or distribute malware.
Methods and Techniques of Switch Spoofing: How Does Switch Spoofing Work
Switch spoofing attacks involve exploiting vulnerabilities in network switches to impersonate legitimate devices on a network. Attackers employ various methods and techniques to achieve this:
One common technique is MAC address spoofing. Attackers use tools or scripts to change the MAC address of their network interface card (NIC) to match that of a legitimate device on the network. By doing so, they can trick the switch into believing that their device is authorized to access the network and communicate with other devices.
ARP Poisoning
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) poisoning is often used in conjunction with MAC address spoofing. Attackers send malicious ARP messages to the network, claiming to be the legitimate MAC address for a particular IP address. This causes other devices on the network to update their ARP tables, associating the attacker’s MAC address with the victim’s IP address.
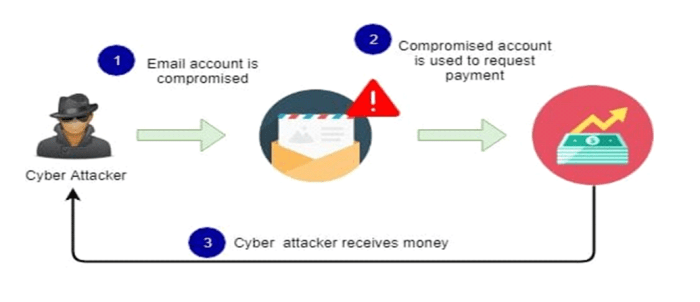
Switch spoofing is a technique that allows an attacker to impersonate another switch on a network. This can be used to launch a variety of attacks, such as man-in-the-middle attacks or denial-of-service attacks. In one notable case, a woman weighing 55 kilograms demonstrated the principles of switch spoofing , highlighting the potential impact of this technique.
As a result, traffic intended for the victim is misdirected to the attacker’s device.
Impact and Consequences of Switch Spoofing
Switch spoofing poses severe threats to network security, leading to a range of adverse consequences:
Disruption of Network Traffic
By impersonating legitimate network devices, attackers can manipulate traffic flow, causing disruption and denial of service. They can redirect traffic to unauthorized destinations, creating congestion and preventing legitimate users from accessing network resources.
Data Theft
Switch spoofing allows attackers to intercept and eavesdrop on network traffic, potentially exposing sensitive data. They can capture login credentials, financial information, and other confidential data transmitted over the network.
Compromised Network Integrity
Switch spoofing undermines the integrity of the network by introducing unauthorized devices and manipulating traffic. Attackers can gain unauthorized access to network resources, modify configurations, and even launch other cyberattacks.
Facilitation of Other Cyberattacks
Switch spoofing can facilitate a wide range of cyberattacks, including man-in-the-middle attacks, denial-of-service attacks, and malware distribution. By impersonating trusted devices, attackers can bypass security controls and gain a foothold in the network.
Detection and Prevention of Switch Spoofing
Switch spoofing attacks can be detected through various methods, including network monitoring tools and intrusion detection systems (IDS). These tools monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns and activities that may indicate a switch spoofing attack. They can detect anomalies such as MAC address conflicts, IP address spoofing, and ARP poisoning attempts.
Network Monitoring Tools
Network monitoring tools provide real-time visibility into network traffic, allowing administrators to identify unusual behavior or changes that may indicate a switch spoofing attack. These tools can monitor MAC addresses, IP addresses, and ARP tables to detect inconsistencies or unauthorized modifications.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), How does switch spoofing work
IDSs are designed to detect and alert on security threats and anomalies. They can be configured to monitor network traffic for specific signatures or patterns associated with switch spoofing attacks. IDS can identify and block malicious traffic, preventing it from reaching the network infrastructure.
Best Practices for Prevention
In addition to detection methods, several best practices can help prevent switch spoofing attacks:*
-*Switch Configuration
Implement strong switch configurations, including MAC address filtering, port security, and DHCP snooping. These measures can restrict unauthorized access to the network and prevent attackers from modifying switch settings.
-
-*Network Segmentation
Divide the network into smaller segments using VLANs or subnets. This limits the impact of a switch spoofing attack to a specific segment, preventing it from spreading across the entire network.
-*Regular Monitoring and Audits
Regularly monitor network traffic and perform security audits to identify any suspicious activities or vulnerabilities that could be exploited for switch spoofing attacks.
-*Software Updates
Keep network devices and software up to date with the latest security patches and firmware updates to address known vulnerabilities that could be used in switch spoofing attacks.
FAQ Overview
What is switch spoofing?
Switch spoofing is a technique used by attackers to impersonate legitimate network devices by manipulating MAC addresses, enabling them to gain unauthorized access to networks and intercept sensitive data.
How does switch spoofing work?
Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in network switches to send spoofed MAC addresses, tricking the switch into believing that they are authorized devices. This allows them to bypass security measures and gain access to the network.
What are the consequences of switch spoofing?
Switch spoofing can lead to network traffic disruption, data theft, and compromised network integrity. It can also facilitate other cyber attacks, such as man-in-the-middle attacks and denial-of-service attacks.
How can I prevent switch spoofing?
Implement robust switch configurations, including strong password protection and MAC address filtering. Regularly monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and deploy intrusion detection systems to detect and respond to potential attacks.
