Horizontal shrink by a factor of 1/3 – Horizontal shrinkage by a factor of 1/3, a fundamental concept in design and engineering, unveils a world of possibilities and applications. This detailed guide delves into the intricacies of horizontal shrinkage, exploring its applications, methods, impact on design, and advanced techniques, empowering readers with a comprehensive understanding of this versatile concept.
From its inception to its practical implementations, horizontal shrinkage by a factor of 1/3 has garnered significant attention, and this guide serves as a valuable resource for professionals and enthusiasts alike.
1. Horizontal Shrinkage by a Factor of 1/3
Horizontal shrinkage refers to the reduction in the width of a material or object along the horizontal axis. When applied to a factor of 1/3, it indicates a reduction in width by one-third of the original measurement.
To illustrate, if a material initially measures 9 units wide, horizontal shrinkage by a factor of 1/3 would reduce its width to 6 units.
This concept is commonly used in various industries and applications, such as textiles, printing, and engineering.
2. Applications of Horizontal Shrinkage
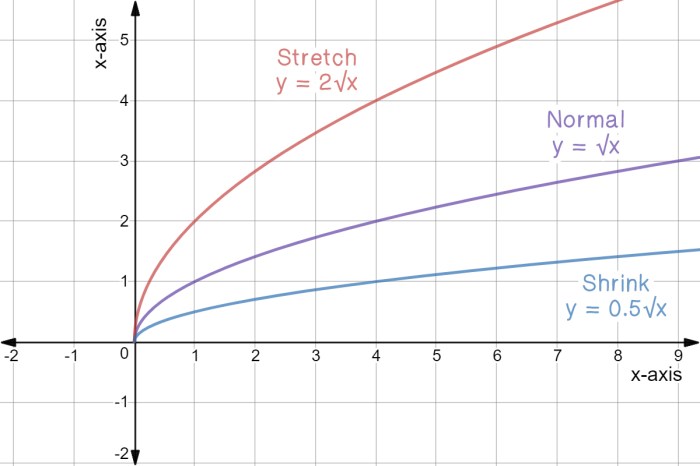
Textiles
- Shrinkage is used to create desired textures, reduce wrinkles, and improve fabric stability.
- Different fibers and fabrics exhibit varying shrinkage rates, requiring careful consideration during garment manufacturing.
Printing
- Horizontal shrinkage is accounted for during printing to ensure accurate alignment and avoid distortion of images or text.
- It is essential to understand the shrinkage properties of the paper or material being used to prevent errors.
Engineering
- Horizontal shrinkage is considered in the design of bridges, buildings, and other structures to ensure stability and prevent cracking.
- Materials like concrete and steel exhibit different shrinkage rates, which must be accounted for in construction calculations.
3. Methods for Achieving Horizontal Shrinkage
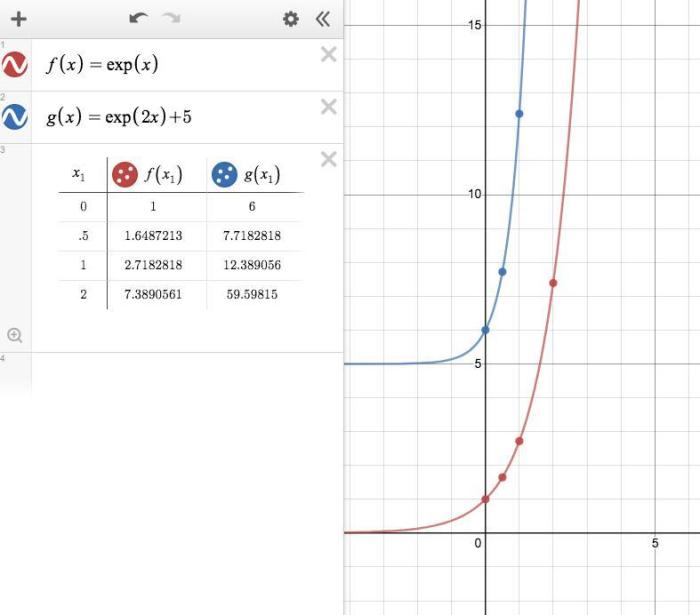
Heat Treatment, Horizontal shrink by a factor of 1/3
- Exposing materials to heat can cause fibers to contract, resulting in horizontal shrinkage.
- The temperature and duration of heat treatment must be carefully controlled to achieve the desired shrinkage factor.
Chemical Treatment
- Certain chemicals, such as chlorine and sodium hydroxide, can induce shrinkage in materials.
- The type of chemical used and the concentration of the solution determine the extent of shrinkage.
Mechanical Stretching
- Stretching materials along the horizontal axis can cause permanent shrinkage.
- This method is often used in the production of textiles to create specific textures or dimensions.
4. Impact of Horizontal Shrinkage on Design
Layout and Proportions
- Horizontal shrinkage can affect the overall layout and proportions of designs.
- Designers must consider the potential shrinkage of materials when determining the dimensions and spacing of elements.
Functionality
- Shrinkage can impact the functionality of designs, particularly in moving parts or mechanisms.
- Accurate calculations are crucial to ensure that components fit together properly and function as intended.
5. Tools for Implementing Horizontal Shrinkage
| Tool | Features | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shrinkage Calculator | Calculates shrinkage based on material properties and treatment parameters | Quick and easy to use | May not be accurate for all materials |
| Shrinkage Tester | Measures the actual shrinkage of materials | Provides precise measurements | Can be time-consuming and expensive |
| Heat Gun | Applies heat to induce shrinkage | Versatile and portable | Requires careful temperature control |
6. Advanced Techniques in Horizontal Shrinkage
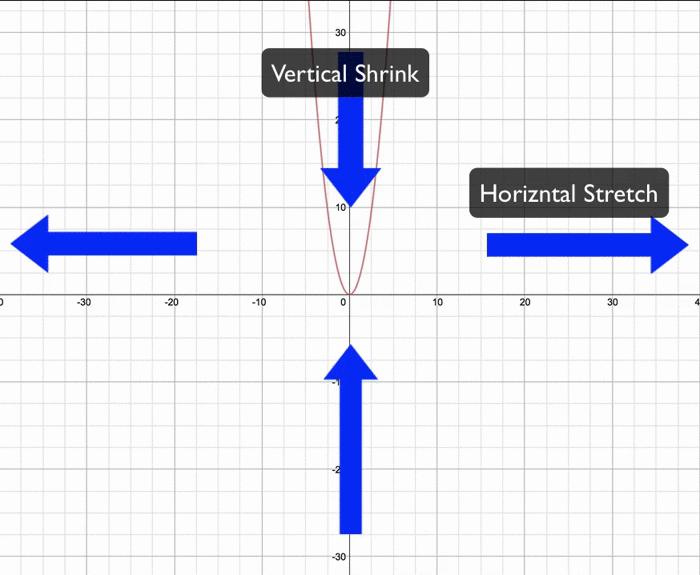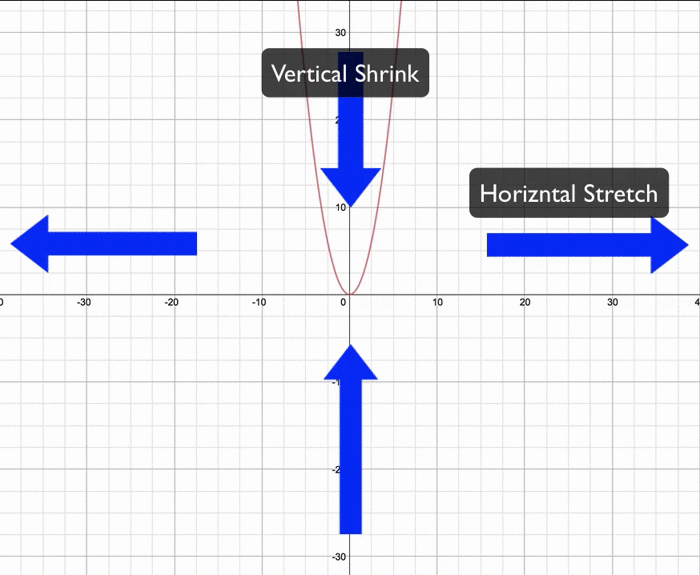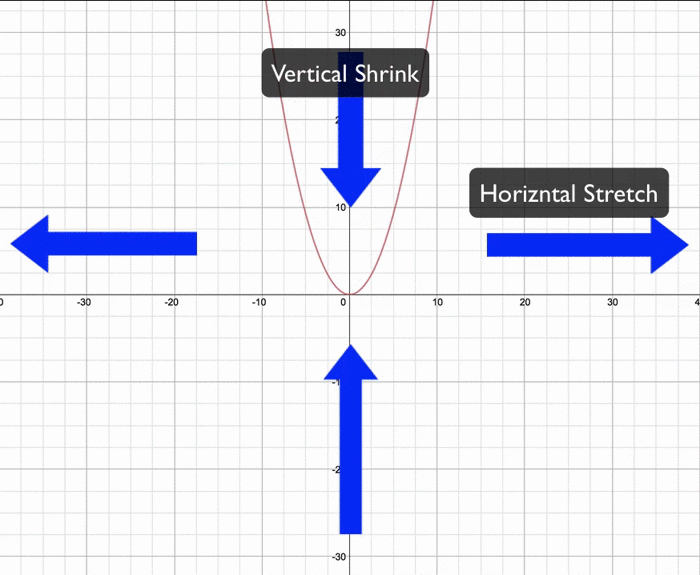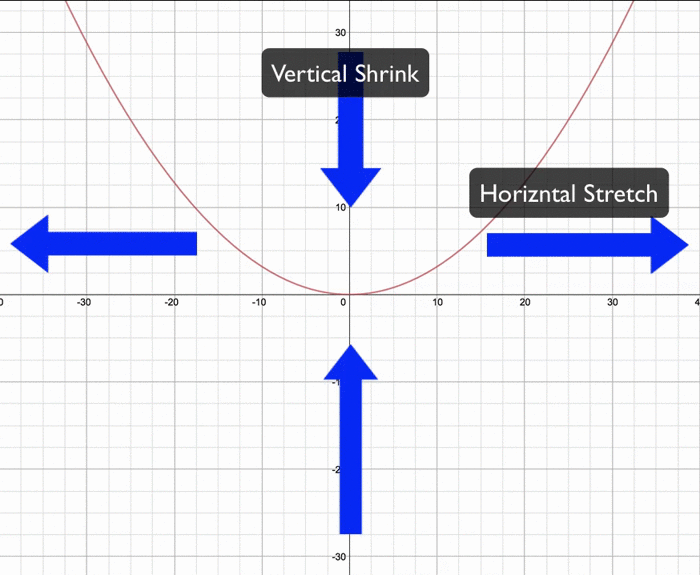
Anisotropic Shrinkage
- Materials can exhibit different shrinkage rates along different axes.
- Advanced techniques consider this anisotropy to achieve precise shrinkage in specific directions.
Computer Modeling
- Computer models can simulate shrinkage behavior based on material properties and treatment conditions.
- This allows for optimization of shrinkage processes and accurate predictions of final dimensions.
User Queries: Horizontal Shrink By A Factor Of 1/3
What is the significance of horizontal shrinkage by a factor of 1/3?
Horizontal shrinkage by a factor of 1/3 plays a crucial role in various fields, including design and engineering, where it allows for precise scaling and manipulation of space.
How does horizontal shrinkage impact design considerations?
Horizontal shrinkage can significantly affect design considerations, influencing the overall layout, proportions, and functionality of designs.